Credits: picture from http://www.city.yokohama.lg.jp/ondan/english/yscp/
| Country | Japan | |
| City | Yokohama | |
| Name | Yokohama Smart City Project | |
| Date | 2010 | |
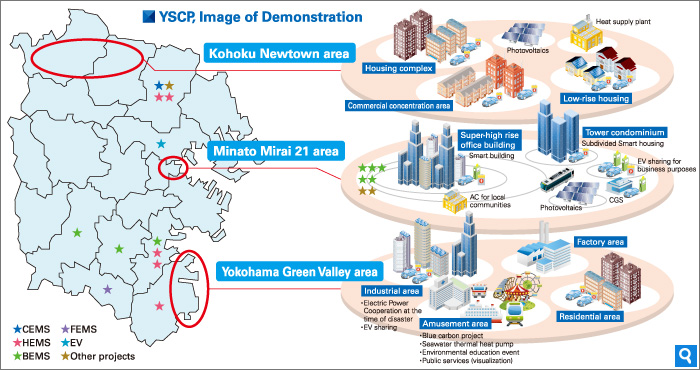
| Description | Yokohama Smart City Project (YSCP) aims to build a smart city having the ability to support the mass introduction of renewable energy as well as to ensure the stable energy supply across the municipal area even in time of crisis.
More specifically, the Yokohama Smart City Project is a five-year pilot program with a consortium of seven Japanese companies – Nissan Motor Co., Panasonic Corp., Toshiba Corp., Tokyo Electric Power Co., Tokyo Gas Co., Accenture’s Japan unit and Meidensha Corp. In 2010, the City of Yokohama formulated the Yokohama Smart City Project (YSCP)to run in three Yokohama city districts and it has since been deployed to the entire city with a project area covering about 435 km2. The project applies smart grids for the energy management of households, buildings and local communities, introduces large scale renewable energy, and promotes next generation transport systems in order to demonstrate new urban management forms. The project’s mission is to establish a social system that can sustainable develop in an already established city. In order to achieve this, the city introduced a Community Energy Management System (CEMS) to achieve efficient energy management by linking each EMS, such as in homes and buildings, and stationary energy storage. Specific goals include:
In addition, the city will provide 2,000 electric vehicles and charging stations for the transport sector. The use of renewable energy sources is also a priority for the city, as is an effort to change the way citizens relate to energy use. Solar power generation in 249 locations, wind power generation in 2 locations, hydropower generation in 3 locations, and biomass power generation in 6 locations will be implemented. In addition, consumers will receive incentives to limit electricity use, thus contributing to the reduction of CO2 at a lower social cost. |
|
| Urban Co-Governance | Weak | |
| Enabling State | Moderate | |
| Pooling | Strong | |
| Experimentalism | Moderate | |
| Tech Justice | Moderate | |
| Project Website | http://www.city.yokohama.lg.jp/ondan/english/yscp/ | |
| References, sources, contact person(s) | Websites
To contact in Japanese only : ss-seisaku@city.yokohama.jp Or in English : callcenter@city.yokohama.jp |
|
yokohama